Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1

Type 1 diabetes type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
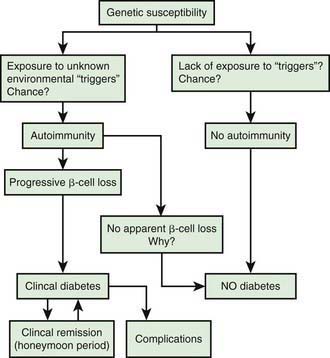
Schematic diagram pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus type 1. It develops when the body s immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells the only cells in the body that make the hormone insulin which regulates blood glucose. Pathophysiology of diabetes type 1. The pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus suggests that it is an autoimmune disease wherein the body s own immune system generates secretion of substances that attack the beta cells of the pancreas. For effective understanding medicine has had pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus made easy by grouping into three categories they are an autoimmune mechanism genetic considerations environmental factors.
A common distinction is made between type a accounting for up to 90 of overall. Type 1 diabetes is more common among children and young adults around 20 years. Though diagnosis of type 1 diabetes frequently occurs in childhood 84. Type 1 diabetes is due to pancreatic islet b cell destruction.
Type i diabetes mellitus formerly referred to as juvenile onset diabetes mellitus or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. The two types of diabetes mellitus are differentiated based on their causative factors clinical course and management. Only 5 of people with diabetes have this form of the disease. Diabetes has major classifications that include type 1 diabetes type 2 diabetes gestational diabetes and diabetes mellitus associated with other conditions.
Regardless of the pathophysiology of diabetes chronic high blood. It is classified as type 1 insulin dependent or juvenile onset diabetes and type 2 non insulin dependent or also called as insulin resistant disease. Diabetes pathophysiology diseases process diagram diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of absolute or relative insulin deficiency or resistance. It is now well recognised that t1dm is an autoimmune disorder characterised by the destruction of insulin producing pancreatic β cells 17 like many other immune mediated diseases t1dm shows heterogeneity in terms of age of onset severity of autoimmune response and efficacy of therapy.
Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus type 1 diabetes mellitus is a chronic autoimmune disease associated with selective destruction of insulin producing pancreatic β cells figure 1. Pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes condition is by large characterized by a deficiency of insulin hormone. As we learn more about the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus we find that. Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Nonimmune type 1b diabetes occurs secondary to other diseases and is much less common than autoimmune type 1a. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate protein or fat metabolism. This condition is known to occur at any age group but the majority of affected individuals are diagnosed in their mid teenage years.