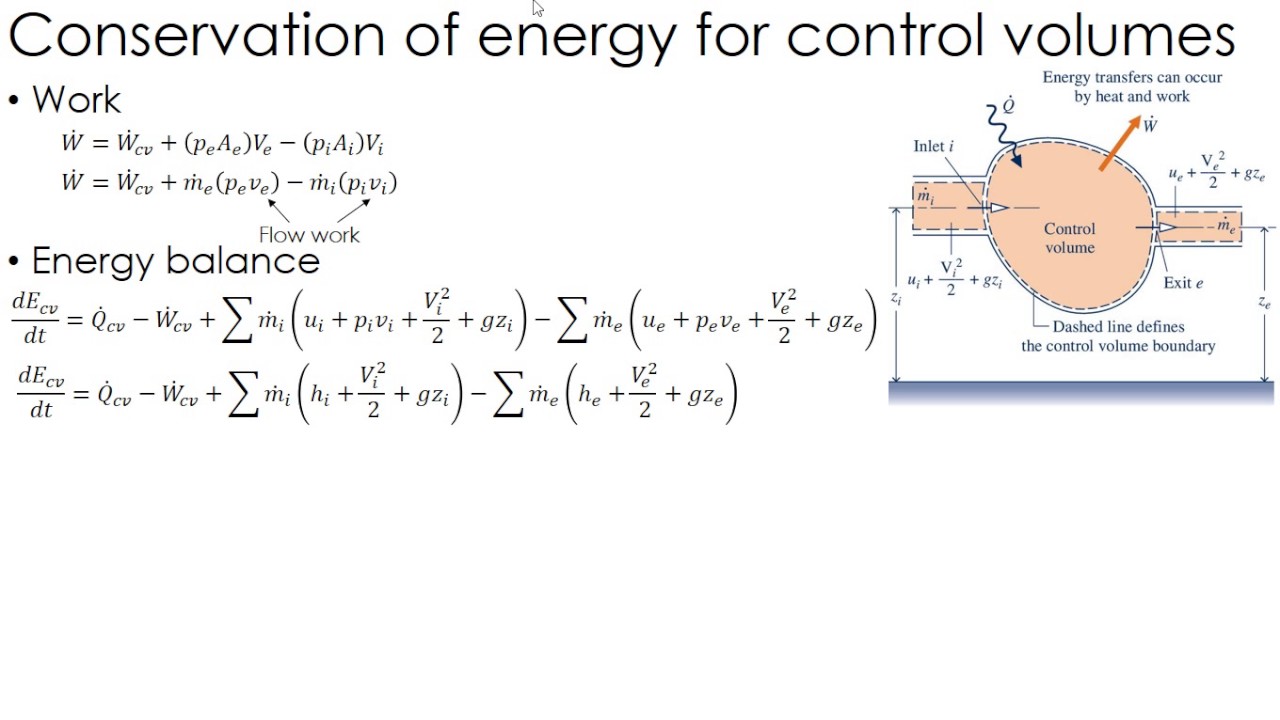
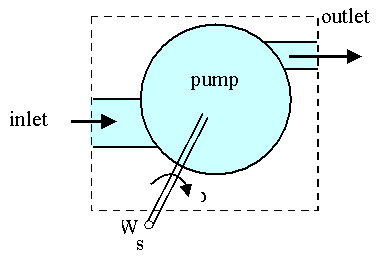
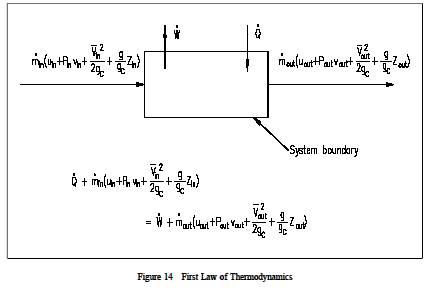
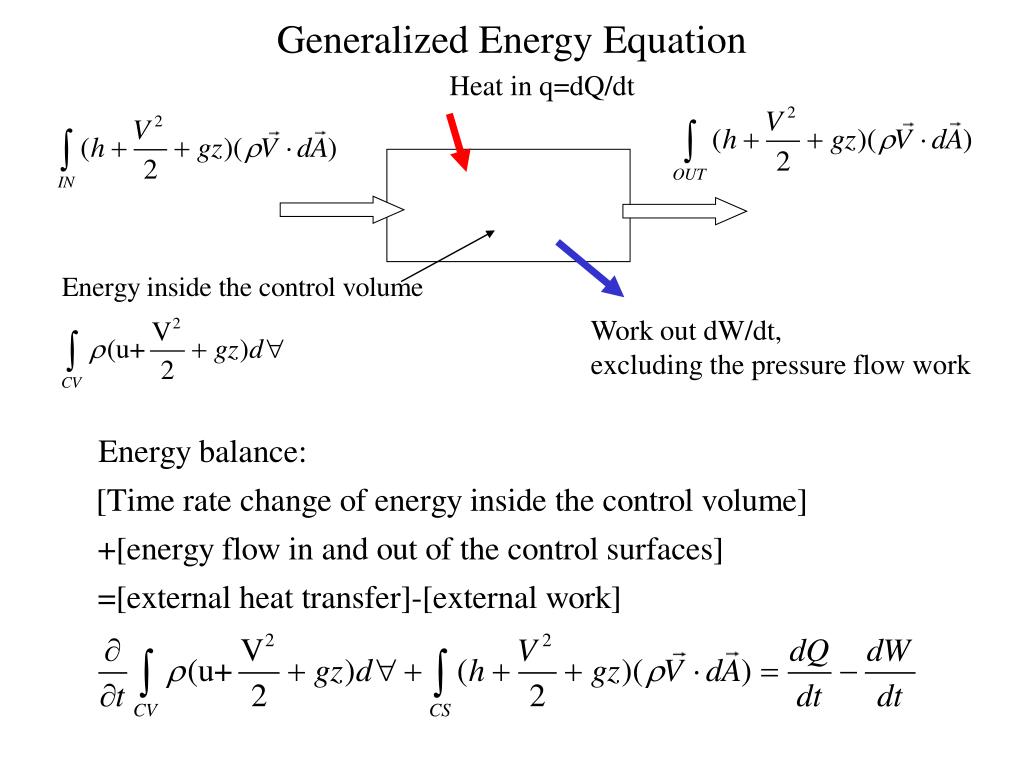
Energy Balance Equation For Control Volume
The energy equation for control volumes recall the first law of thermodynamics.
Energy balance equation for control volume. In our derivation of the mass balance equation we have referred to the mass of pollutant in a lake and the fluxes of pollutant into and out of. Furthermore with a constant mass flow rate it is more convenient to develop. De cv dt q w m. Consider the control volume shown in the following figure.
Under steady flow conditions there is no mass or energy accumulation in the control volume thus the mass flow rate applies both to the inlet and outlet ports. Where rate of change of total energy of the system rate of heat added to the system rate of work done by the system. Conservation of energy if the control volume contains multiple inlets exits then we may write. Control volume energy balance duration.
Eq 6 m ρva m ρ v a ρ ρ density eq 7 emass mφ e m a s s m φ. At this point it is the net work transfer. 115 videos play all egr 263 thermodynamics uwmc engineering. Uwmc engineering 5 135 views.
The physical idea is that any rate of change of energy in the control volume must be caused by the rates of energy flow into or out of the. The complete energy equation for a control volume. We must now consider what the work term really represents. Net quantity of energy entering to the control volume net quantity of energy leaving the control volume rate of net energy entering to the control volume rate of net energy leaving the control volume where h1 and h2 are enthalpy and z1 and z2 are the distance of entrance and exit section of control volume from datum line as shown in figure.
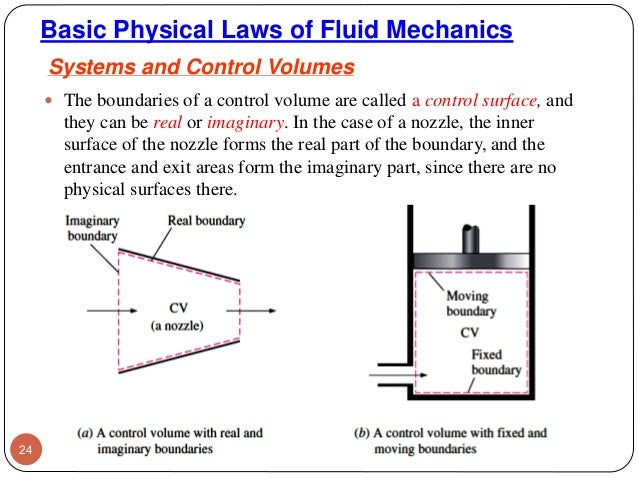
A mass balance is only meaningful in terms of a specific region of space which has boundaries across which the terms and are determined. Sum of the rate of mass flowing into the control volume sum of the rate of mass flowing from the control volume time rate of change of the mass inside the control volume calculating the flow ratesession 8 v v a m v a rr r r ρ v va. To derive the first law as a rate equation for a control volumewe proceed as with the mass conservation equation.