Thiazide Treatment Of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus

Acetazolamide might be an option to treat lithium induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus patients who fail to respond to standard treatment.
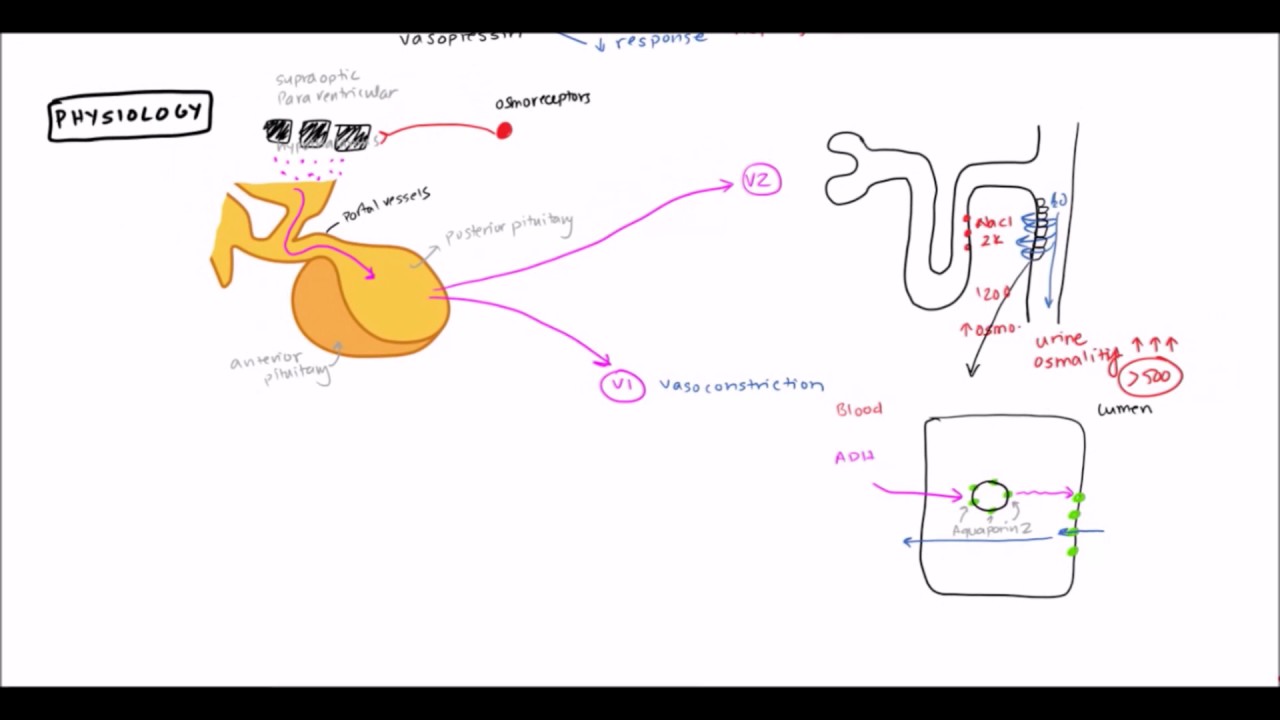
Thiazide treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Waldhauser department of pediatrics university of vienna währinger gürtel 18 20 a 1090 vienna austria. It also caused an increase in the abundance of enac channels. In rates with lithium induced nephrogenic di hctz reversed lithium induced downregulation of aqp2. Response to indomethacin and hydrochlorothiazide in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs nsaids like ibuprofen motrin indomethacin indocin and naproxen. Treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus with prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors. However the treatment of this drug. Desmopressin diabetes insipidus lithium indomethacin polyuria thiazide diuretics lithium carbonate is a well documented cause of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus with as many as 10 to 15 of patients taking lithium developing this condition.
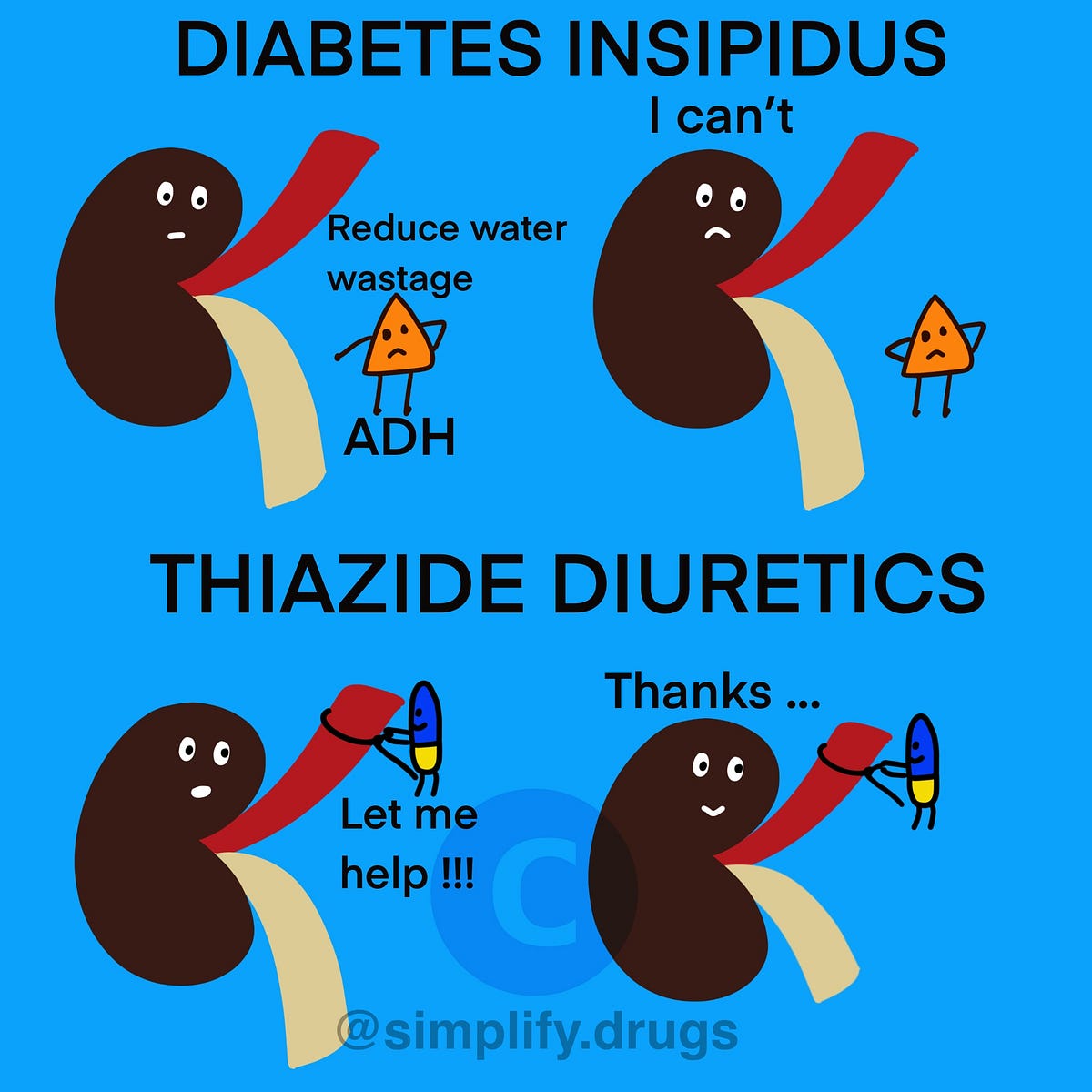
The only therapeutic approach is sodium restriction or administration of thiazide diuretics or both. Libber s harrison h spector d. In 1905 meyer in was the first to observe that diuretics decrease urinary volume in diabetes insipidus but it was only in 1959 that crawford and kennedy used thiazides to. If you have more severe nephrogenic diabetes insipidus you may be prescribed a combination of thiazide diuretics and a non steroidal anti inflammatory drug nsaid to help reduce the amount of urine your kidneys produce.
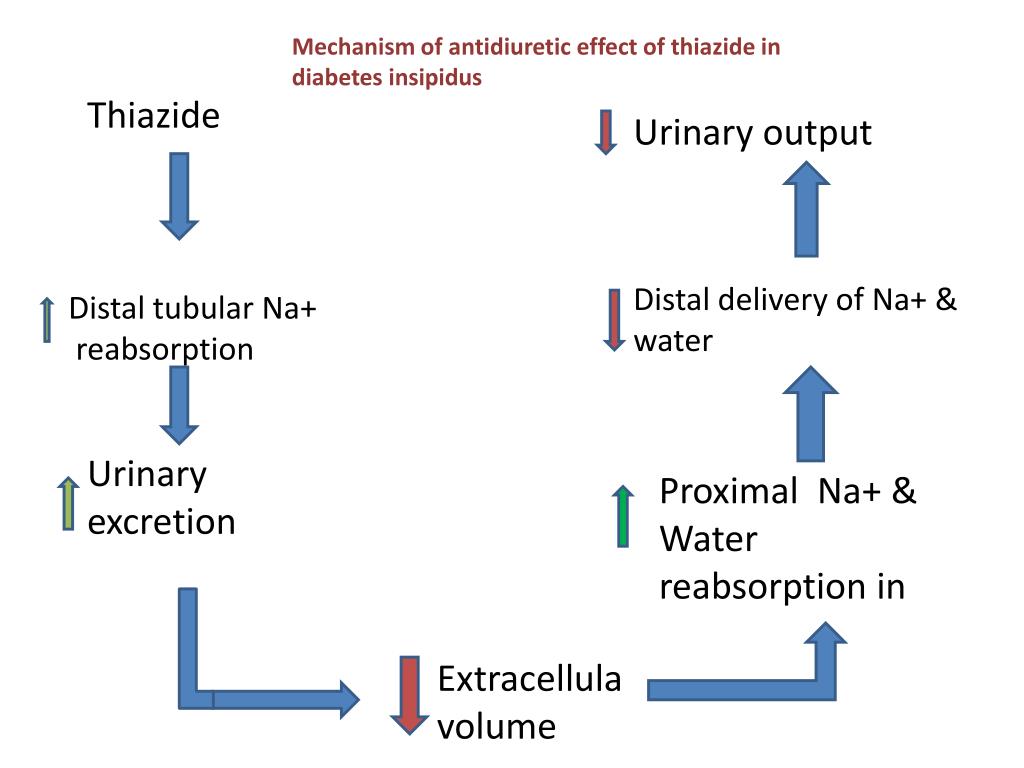
Thiazide diuretics control hypertension in part by inhibiting reabsorption of sodium na and chloride cl ions from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys by blocking the thiazide sensitive na cl symporter. Seidl and f. Some treatments can reduce the symptoms of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus at least somewhat. Treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus with hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride v.
Clinicians have been well aware of lithium toxicity for many years. Monnens l jonkman a thomas c. It might seem. While these results are specific to li induced renal effects they may at least partially explain how a thiazide can serve to decrease polyuria in patients with diabetes insipidus.