Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2

Beyond the duo insulin resistance secretion deficit.
Schematic diagram pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus type 2. In type 2 diabetes either the body does not produce enough. Carrera boada ca 1 martínez moreno jm. An absolute or relative insulin deficiency. Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus type 2.
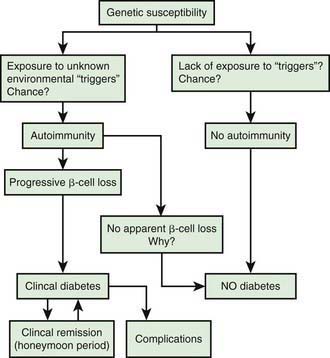
The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by peripheral insulin resistance insulin insensitivity cell damage glucose transport glut4 dysfunction and impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production. This condition is known to occur at any age group but the majority of affected individuals are diagnosed in their mid teenage years. Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin. It is classified as type 1 insulin dependent or juvenile onset diabetes and type 2 non insulin dependent or also called as insulin resistant disease.
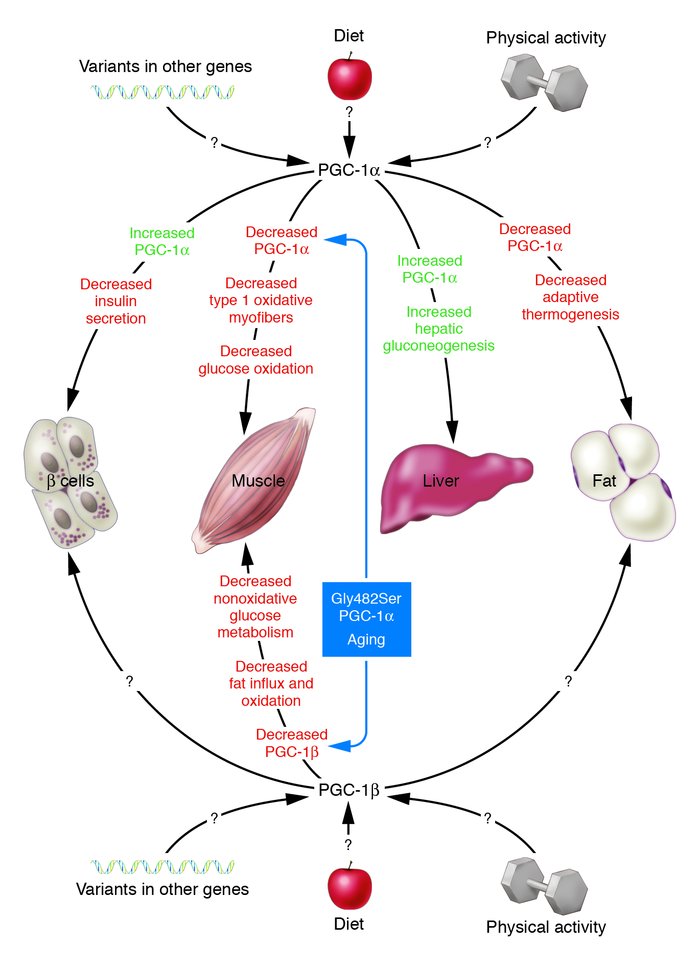
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is often associated with certain genetic predispositions environmental factors lifestyle choices and the dynamic interactions between all of these different aspects. B 4 physiology and biomedical research unit department of biological sciences college of basic and applied sciences. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate protein or fat metabolism. Type i diabetes mellitus formerly referred to as juvenile onset diabetes mellitus or insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.
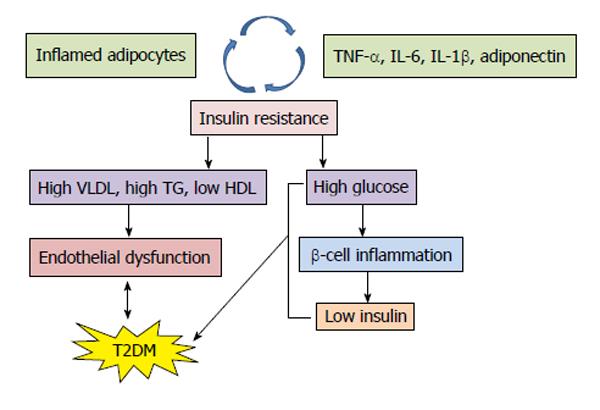
Exactly why this happens is unknown although genetics and environmental factors such as being overweight and inactive seem to be contributing factors. For example one of the vicious cycles occurs when high blood sugar leads to insulin resistance. Extracellular hyperglycemia and intracellular hypoglycemia. Reduced tissue utilization of glucose.
San bernardino caracas venezuela. Diabetes pathophysiology diseases process diagram diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of absolute or relative insulin deficiency or resistance. Pathophysiology of diabetes type 1. 1 department of endocrinology hospital de clínicas av.
Pathophysiology of diabetes. Pathophysiology review the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus ozougwu j. The following diagram shows how type 2 diabetes is a series of vicious cycles that fuel each other enabling the disease to develop and progress deteriorating the body over a period of many years. The causes of type 2 diabetes are multi factorial and include both genetic and environmental elements that affect beta cell function and tissue muscle liver adipose tissue and pancreas insulin sensitivity.
D 3 and unakalamba c. Type 2 diabetes type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes.